What is Command Prompt/CMD?
Command Prompt (CMD) is a command-line interpreter application available in most Windows operating systems. Usually, we use it to execute entered commands. Most of those commands automate tasks via scripts and batch files, perform advanced administrative functions, and troubleshoot or solve certain kinds of Windows issues.
Besides that, Command Prompt is officially called Windows Command Processor, but sometimes we refer it to as the command shell or cmd prompt, or even by its filename, cmd.exe.
Moreover, it is sometimes incorrectly referred to as “the DOS prompt” or as MS-DOS itself. Command Prompt is a Windows program that emulates many of the command line abilities available in MS-DOS. However, it’s not MS-DOS.
Cmd is also an abbreviation for many other technical terms. For example, a centralized message distribution, color monitor display, and common management database. However, none of them have anything to do with Command Prompt.
How to Launch Windows Command Prompt
To launch Windows Command Prompt (CMD), please do the following: Go to Windows –> Run (by press “Windows” key + “R” key) –> Type “CMD” and hit “ENTER”
Some Useful Commands in Command Prompt
Command Prompt has a lot of the commands syntax. Their availability was differs from one operating system to the others. Furthermore, there are a lot of commands that you can use, but not all of them are utilised as frequently as others.
Here are a few of the most helpful Command Prompt commands that you can use in various situations. chkdsk, copy, ftp, del, format, ping, attrib, net, dir, help, and shutdown are among the commands.
Help
The most crucial Command Prompt command is probably help. You can get a list of available commands by typing “help.” If you remember nothing else from this tutorial, keep in mind that if you ever get stuck in a CMD rabbit hole, “help” is only four letters away.
Tracert
Should you monitor the internet traffic on your computer? This command is ideal for keeping track of how many intermediate servers your packets pass through. It also keeps note of the amount of time each transfer takes and the server’s name or IP address.
IPConfig
IPConfig will come in handy for a variety of reasons if you have networking troubles. Running it gives you a lot of information about your PC and local network, such as your router’s IP address, the operating system you’re using at the time, and the status of your various network connections.
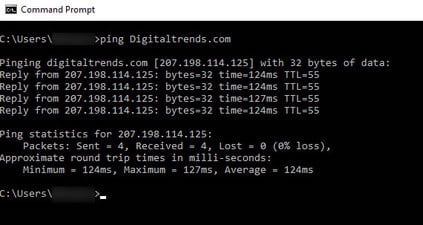
Ping
Do you want to know if your internet is down for good or if it’s just a software issue that’s causing the problem? Something should be pinging. Whether it’s Google.com or your own own remote server, it doesn’t matter. Whatever method you use, if you receive a response, you know there is a connection. This command can also be used to see if local network systems are up and running.
Chkdsk
Check Disk, written as “Chkdsk,” examines your selected drive for problems. Although there are other Windows and third-party tools for inspecting a drive for faults, Check Disk is a tried-and-true classic that works well and may save you from losing data if a problem is detected early enough.
SFC
The programme “SFC /scannow,” which stands for System File Checker, will scan all of the Windows system files for faults and, if possible, repair them. This one is going to take a while.
Cls
The outputs of Command Prompt commands are valuable, but they aren’t properly organised or easy to understand. To clean the screen if it becomes too cluttered, type “Cls” and hit enter.
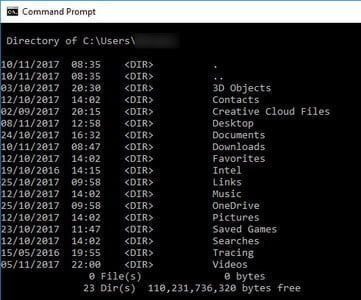
Dir
If you’re browsing your file system with the Command Prompt, the “Dir” command will show you all of the files and directories in the current folder. When you want to find something specific, you can also add a /S and utilise it as a search.
Netstat
This function displays information about your PC’s existing connections, such as TCP connections, ports on which your system is listening, Ethernet statistics, and the IPRouting table.
Exit
This accomplishes exactly what you’d expect. You don’t want to use your mouse, or you can’t seem to find the “X” in the top-right corner? To exit the Command Prompt, simply type “exit” and press enter.
Tasklist
Tasklist provides you with real-time information on all of the tasks that Windows is now performing. You can utilise switches (such “-m”) to delve deeper into these jobs and how they work, which is highly valuable for identifying any potential issues. It’s no surprise that this is frequently followed by the “Taskkill” command, which is used to force the completion of specified tasks.
Shutdown
Although you don’t have to shut down your Windows 10 computer at night, you can do it using the Command Prompt or the Start Menu. Simply type “shutdown” and press enter, and your computer will go to sleep.


